Best Open-Source Finite Element Analysis Software
This is a review of some of the most up-to-date and actively developed open-source projects in Finite Element Analysis.
In this post we will briefly discuss the main features of various different open-source Finite Element projects and libraries, hopefully helping you decide which one suits your needs best.
Commercial vs Open-Source Simulation Software
The question of which Finite Element Method software to use arises very naturally. The discussion that follows is based on three basic considerations:
- In real applications, very few people write FEM code from scratch anymore.
- Commercial FEM software is usually very easy to use for some predefined cases, but potentially obscure to customize, is very hard to integrate with external tools. Last but not least, it is also very expensive, requirinig companies to pay additional licenses per user or if multiple processors are being employed.
- Open-Source FEM software, as we shall see, has reached a high level of maturity during recent years, but it is generally a lot harder to use than their commercial counterparts.
While we could discuss the issue of open-source vs commercial software in much more detail, it is clear that open-source offers great long-term value for end-users, but there are challenges in making a high-quality open-source scientific software project widely viable beyond academic or expert use.
That being said, let’s go over the main open-source projects for Finite Element Analysis that we are aware of, and typically resort to, and which seem to be under active development and support a sizeable userbase.
This list is by no means exhaustive. If you known about an important and actively developed project, please contact us and we will include the relevant information here.
Elmer

Website: https://www.csc.fi/web/elmer
Elmer is a GPL-licensed multiphyiscs solver based on the Finite Element Method. It includes modules for fluid dynamics, structural mechanics, electromagnetics, heat transfer, acoustics, and others.
The project includes a graphical user interface (ElmerGUI) which is capable of importing meshes in various file formats, set up a PDE system, and exporting the model data and results. Postprocessing is usually done via Paraview.
Fenics Project
Website: https://fenicsproject.org/
The FeniCS project is centered around the numerical solution of Partial Differential Equations (PDE) with the Finite Element Method (FEM). As such, it covers numerous applications ranging from thermomechanics to electromagnetics.
While meshing is performed in third-party libraries such as Gmesh, FeniCS offers high-level Python and C++ interfaces to make the definition and solution of the problem straightforward. Models can be prototyped in workstations or laptops, and later run in clusters with ease.
FeniCSx can be downloaded here. The Python and C++ interfaces is called DOLFINx, and it’s documentation can be found here
FreeFEM
Website: https://freefem.org/
FreeFEM is a library for multi-physics simulation via the Finite Element Method. It includes pre-built physics modules like Navier-Stokes, Linear and Non-Linear Elasticity, thermodynamics, magnetostatics and electrostatics, and fluid-structure interaction.
It also includes its own scripting language to implement new physics modules. It contains its own mesh generation routines, and is also compatible with other open-source tools like Gmsh and Paraview.
Code-Aster: Structural and Thermomechanic Analysis
Website: https://www.code-aster.org
The Code-Aster project, and its associated Salome-Meca software suite was developed by Electricité de France R&D, and in colaboration with Universities and industry. It focuses on solid mechanics, including thermal and mechanical behavior of linear and non-linear materials, and supports static and dynamic analysis. Application areas include fatigue, damage, fracture, and contact mechanics. It also contains modules for geomaterials, porous media, and multi-physics coupling,
The project is used operationally by EDF to justify the lifetime of numerous components and materials used in the nuclear field. As such, it can be applied to analyze machines, pressure vessels and civil engineering structures.
The code is GPL-licensed, and it includes a GUI.
OpenFOAM: Computational Fluid Dynamics
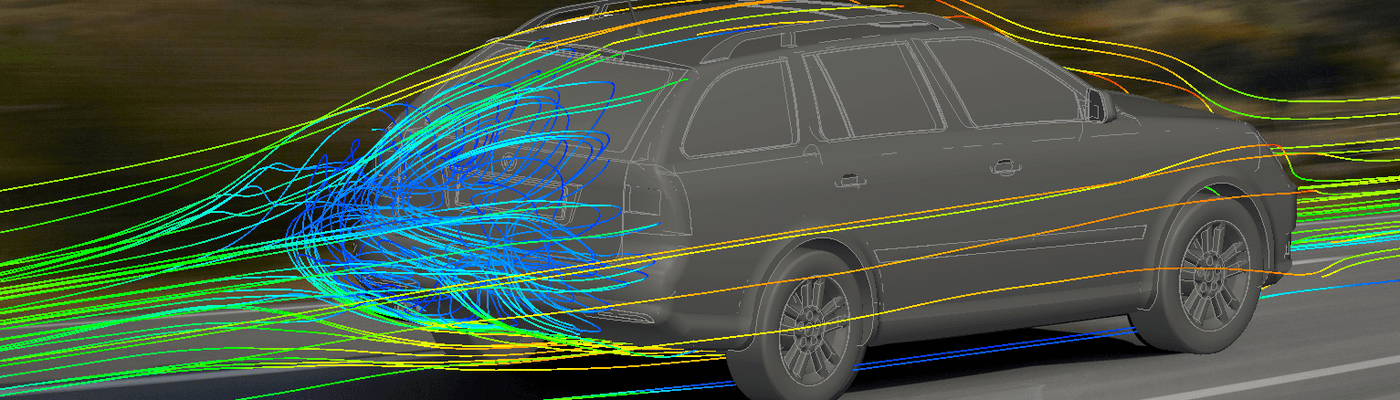
Website: https://openfoam.org/
OpenFOAM is a GPL-licensed project centered around Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD). CFD involves several families of numerical methods, including, but not limited to, Finite Element Methods.
CFD covers a range of scientific and engineering applications. In particular, it is used in many applications that involve heat, thermodynamics, chemistry and solids, such as engines, heat exchangers, electronics cooling, combustion, and so forth.
The software includes its own modules for mesh generation of simple or complex geometries. Post-processing is done via a GUI based on ParaView. Defining a problem and a geometry, on the other hand, is done via scripting.
Deal.II

Supersonic flow around cylinder. Author: Matthias Maier, 10 April 2020. View on Github
Website: https://www.dealii.org
Deal.II is a modern C++ library for solving partial differential equations with the finite element method. It originated from researchers at institutions such as Heidelberg University and Colorado State University and places a strong emphasis on adaptive mesh refinement, parallel computing, and high-order finite elements, making it well-suited for high-performance computing environments.
The library is distributed under the LGPL (version 2.1 or later).
While it does not come with a native graphical user interface, deal.II is often combined with external visualization tools like ParaView or VisIt for post-processing.
MOOSE
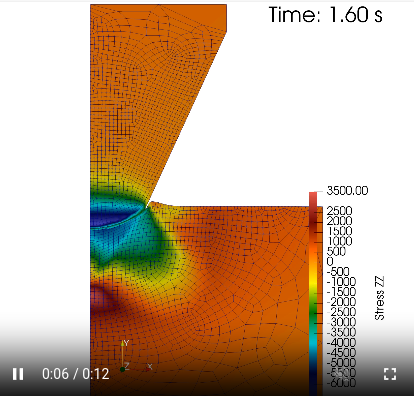
Website: https://mooseframework.inl.gov
MOOSE (Multiphysics Object Oriented Simulation Environment) was designed to streamline the development of sophisticated multiphysics simulations, particularly in the realm of nuclear engineering, but can also handle a wide range of partial differential equation-based problems. It is developed by the Idaho National Laboratory.
MOOSE is released under the LGPL (version 2.1).
MOOSE uses a text-based input system instead of a built-in GUI, relying on established tools such as ParaView for visualization and post-processing.
Master Open-Source FEM for Electromagnetics
Don't Just Run Simulations. Trust Them.
Check out the Course!